Navigating the Pros and Cons of Tesla Yoke Steering Wheel
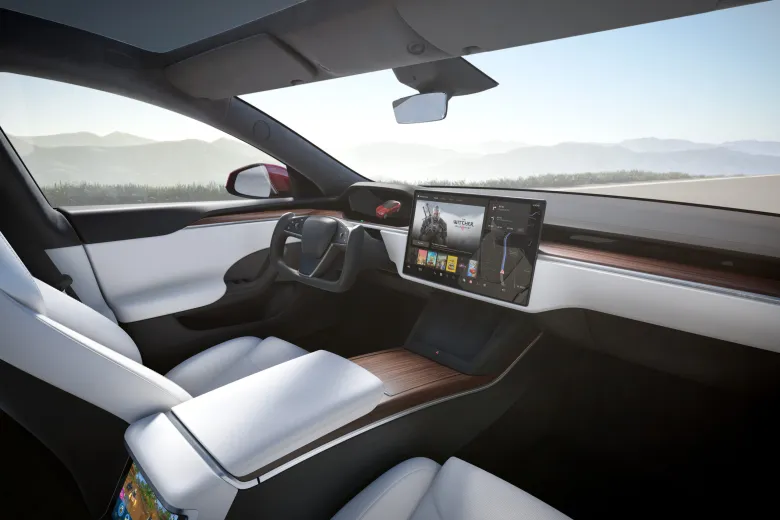
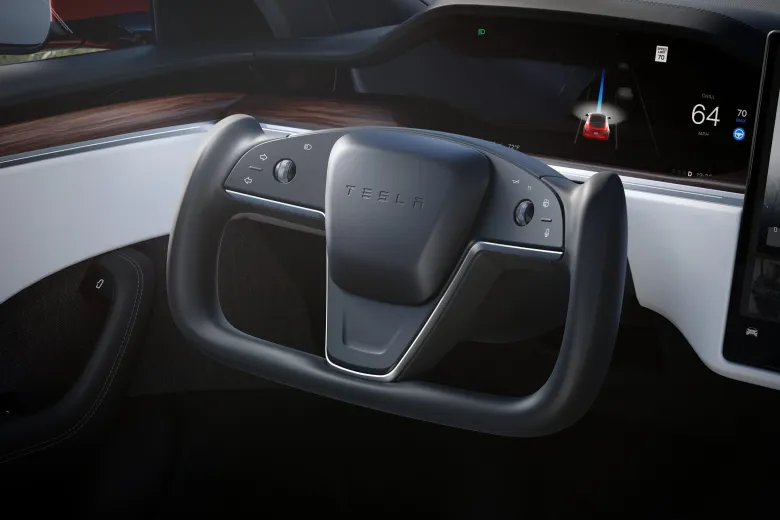
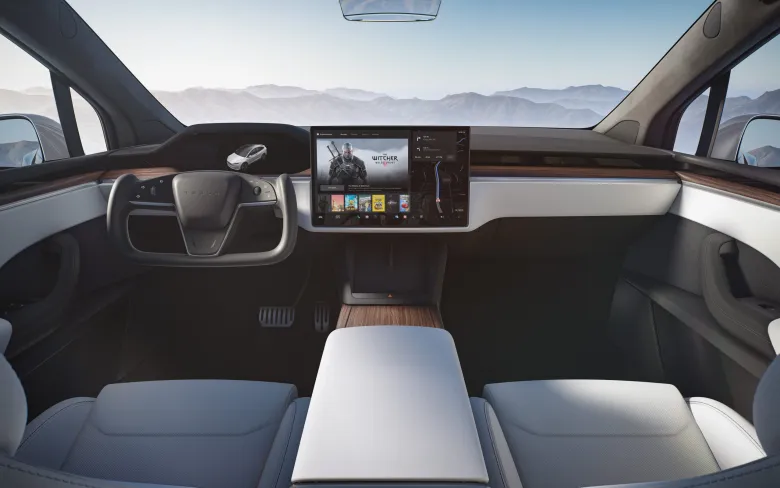
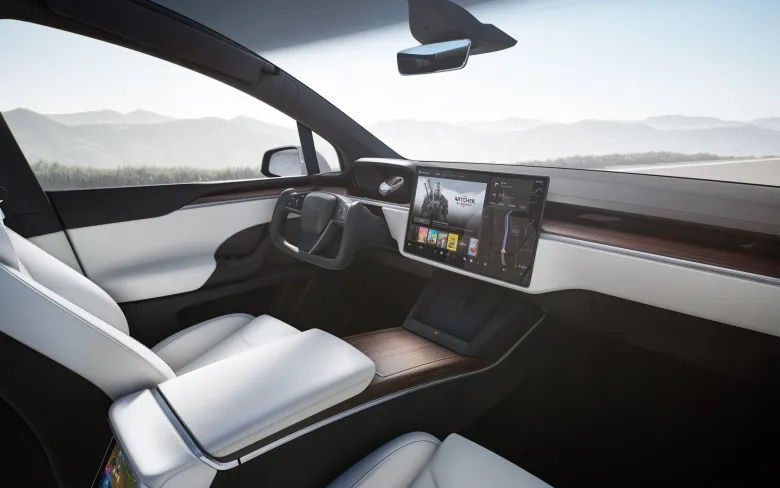
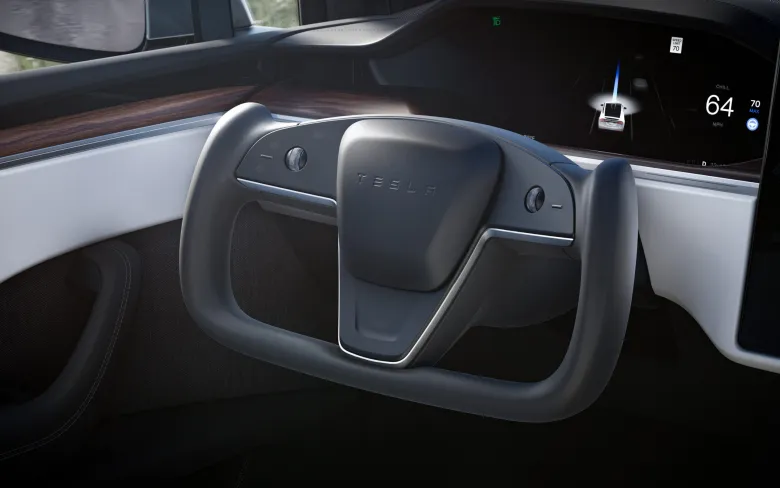
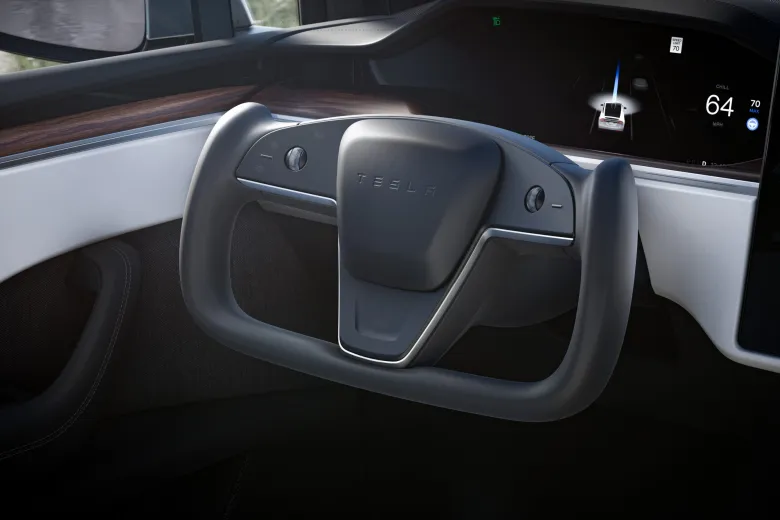
The Tesla Yoke steering wheel, a notable feature in some Tesla electric vehicles, is a radical shift from the conventional circular steering wheels. Its design resembles an aviation yoke, presenting a rectangular shape with rounded corners. This unique design, while innovative, has raised concerns and criticisms among users. Drivers have reported difficulties with basic maneuvers like 90-degree turns or U-turns, attributing these challenges to the Yoke's shape and the amount of turning required compared to traditional wheels. Moreover, the practice of using one's palm to spin the wheel, a technique suggested by some, has been flagged as potentially unsafe.

Tesla might redesign the Yoke or offer alternative steering options due to user feedback and mixed reviews on its practicality for everyday driving.
In response to these concerns, there's speculation that Tesla may consider redesigning the Yoke or introducing alternative steering options. This speculation stems from user feedback and the mixed reception the Yoke has received. Despite its unique appearance and connection to the steering column similar to a regular wheel, the Yoke's practicality in everyday driving has been questioned. There are rumors about Tesla working on a steer-by-wire system to address some of these issues, but as of now, the Yoke's design continues to be a topic of debate among consumers and automotive enthusiasts.
Navigating the Road with the Model S and Tesla Yoke
Tesla is considering redesigning the Yoke or introducing new steering options in response to mixed user feedback and concerns about its everyday practicality.
The Tesla Model S Yoke steering wheel has garnered a diverse range of reactions from users. Criticisms mainly focus on its practicality and safety, with many finding it challenging for basic driving maneuvers like sharp turns. The unconventional design demands more effort to turn than traditional wheels, and there are safety concerns regarding the method of using the palm to spin the wheel. User discussions, including those on Tesla club forums, indicate a hope that regulatory bodies like the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) may intervene to address these issues. The general consensus among critics is that the Yoke's design, requiring 2.3 turns from lock to lock, does not effectively solve any significant problems presented by traditional steering methods.
On the other hand, some users have adapted to the Yoke's unique style, with experiences varying from person to person. Consumer Reports conducted a study involving ten drivers, which highlighted several potential safety pitfalls and little practical benefit, such as difficulties with grip, discomfort during long drives, and confusion over the horn and turn signals. Despite these challenges, other users have appreciated aspects like the improved visibility of the dashboard and speedometer. Anecdotal evidence from some Tesla Model S owners, including older drivers, suggests that with time and adjustment, the Yoke can become a preferable alternative to traditional steering systems. This mixed feedback highlights the Yoke's polarizing nature in the Tesla community.
Tesla Model 3 and Model Y Steering Wheel
Tesla's innovations in steering technology extend beyond the Yoke steering wheel, particularly for Model 3 and Model Y vehicles. Owners of these models now have the option to install a Yoke steering wheel. This steering wheel fits perfectly onto the hub of a Model 3 or Model Y, and some owners have even added a digital screen in front of the steering wheel to mimic the interface of the new Model S. The Yoke design offers a cleaner field of vision for the driver and a wider, flatter base that can serve as a handrest. However, it requires some adjustments for maneuvers like 90-degree turns. The cost for this modification ranges from $1,099-$1,259 USD, depending on the materials chosen, with an additional cost for installation if required.
Tesla's response to practicality concerns and charging cable issues with the Yoke steering wheel, along with the expansion of the V4 Supercharger network, demonstrates their commitment to innovation and customer satisfaction.
The introduction of the Yoke steering wheel was initially met with skepticism due to concerns over practicality. Users pointed out issues with charging cables disconnecting in harsh weather, questioning Tesla's claim of a "best in class user experience." Tesla responded to these concerns, promising action to refine the cable dock and improve flexibility. This responsiveness illustrates Tesla's commitment to addressing user feedback and enhancing customer experience. The expansion of the V4 Supercharger network across Europe and the ongoing upgrades from older versions further reflect Tesla's dedication to innovation and customer satisfaction.
The Ergonomics of Tesla Yoke
The ergonomic and futuristic design of Tesla's Yoke steering wheel has consistently garnered attention since its introduction, with a strong emphasis on enhancing safety and driver visibility. In contrast to the conventional round steering wheels, the Yoke's more compact form substantially improves the driver's perspective of the dashboard and the road ahead. Tesla, renowned for its unwavering commitment to safety, has diligently conducted comprehensive testing to establish the Yoke's reliability across diverse driving scenarios and conditions. This unwavering dedication aligns perfectly with Tesla's ongoing mission to manufacture secure vehicles while relentlessly pushing the boundaries of innovation to harmonize functionality and user experience.
However, the Yoke steering wheel's unconventional design initially raised concerns about its usability and safety. In response, Tesla has actively worked to improve its ergonomics. The Yoke, initially perceived as a risky departure from traditional steering systems, was designed to improve the visibility of the car's wide dashboard screen. Acknowledging the feedback from users and critics, Tesla has implemented updates aimed at enhancing the steering wheel's usability and response, demonstrating the company's responsiveness to consumer needs and its dedication to evolving its vehicle designs for better user experience.
Tesla's Response to Yoke Steering Wheel Criticism
Tesla's response to the criticism surrounding its Yoke steering wheel has been a mix of updates and attempts at improvements, met with varied reactions from users. Consumer Reports highlighted some positive aspects, such as improved visibility of the instrument screen due to the Yoke's design, but also noted drawbacks, including obstruction of the center touchscreen by the Yoke's lower corner. The initial option to choose a traditional wheel over the Yoke was not made available, leading to further user dissatisfaction. In an effort to address these issues, Tesla has released software updates, particularly for the Model S, though the effectiveness of these updates in real-world use remains to be seen.
Further complicating the situation, Tesla's introduction of a new "version H" Yoke aimed to resolve earlier quality issues, but new problems emerged, such as the "Tesla Worm" - a protrusion in the central part of the Yoke. This issue, while aesthetic and not affecting functionality, has become a point of ridicule and underscores ongoing quality control challenges at Tesla. In light of these issues and the rapid sell-out of round steering wheel retrofits, Tesla is reportedly preparing a new Yoke with improved materials to address both durability and usability concerns, reflecting the company's ongoing efforts to refine and improve upon its innovative but controversial Yoke design.
Tesla Yoke vs Traditional Steering Wheel
The introduction of Tesla's Yoke steering wheel marked a significant departure from the traditional round steering wheel, sparking a debate in the automotive world. The Yoke, featured in models like the Tesla Model S and Model X, offers a futuristic aesthetic and enhanced dashboard visibility, thanks to its U-shaped design. This innovative approach eliminates the need for physical stalks and buttons, creating a minimalist and high-tech driving experience. However, it also introduces challenges: drivers face a learning curve adapting to its unconventional shape and touch-sensitive controls, and the lack of tactile feedback can make it less intuitive. Additionally, the physical connection of the Yoke to the front wheels, requiring more than two full rotations for complete steering, leads to discomfort and difficulty in tight turns and low-speed maneuvers.
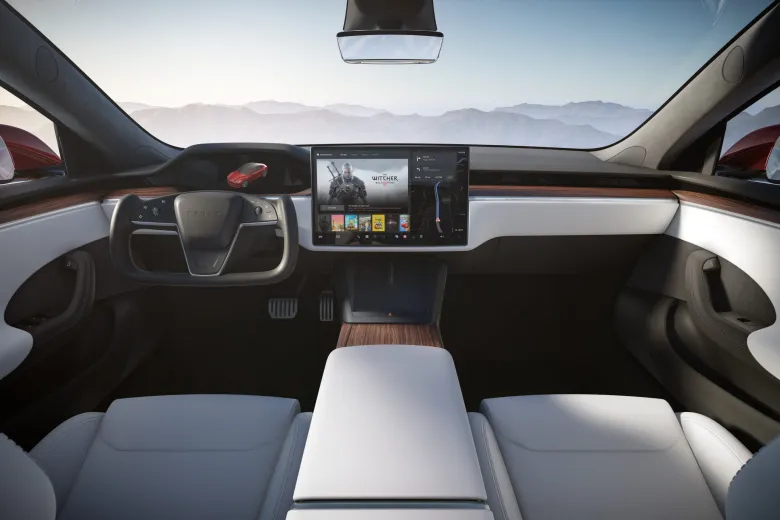

In contrast, traditional circular steering wheels offer familiarity and comfort, with physical controls providing tactile feedback. Their design has been standard for decades, allowing for easy hand-over-hand movement necessary for larger steering inputs. However, they can partially obstruct the driver’s view of the vehicle’s dashboard and touchscreen display. Following Tesla's lead, Lexus introduced a steer-by-wire system in the RZ electric SUV, which significantly reduces the steering rotation required and addresses some of the ergonomic issues presented by the Yoke. This system contrasts sharply with Tesla’s approach, highlighting the varying strategies of automakers in evolving steering wheel design. As such, the choice between a Yoke and a traditional steering wheel largely depends on the driver's preference for innovation versus comfort and familiarity.
Tesla's Vision for Driving Experience and The Role of Steering in Autonomous Cars
Tesla's journey towards fully autonomous driving is deeply rooted in its technological advancements, particularly with the development of its custom AI chip, Dojo. This supercomputer is a cornerstone in Tesla’s strategy, aimed at processing vast amounts of video data to train neural networks for self-driving capabilities. As part of this vision, Tesla emphasizes the role of continuous Over-The-Air (OTA) software updates, which are crucial for enhancing Autopilot functionality and keeping vehicles abreast with the latest improvements. This approach demonstrates Tesla's dedication to leveraging software innovations to progress towards more reliable and safer autonomous vehicles, aligning with its broader mission of transforming transportation.
However, Tesla's approach, particularly its reliance on a camera-only system for Full Self-Driving (FSD), has been subject to scrutiny and skepticism. Critics, including computer-vision specialists, argue that this methodology is fundamentally flawed compared to the complexities of human vision, raising concerns about the efficacy and safety of such systems. This criticism extends to Tesla’s marketing of its Autopilot system, which has been contested for implying capabilities beyond its current technological reach. The naming of the system as "Autopilot" rather than something more representative like "Copilot" has been a point of contention, reflecting the gap between Tesla's ambitious vision and the current reality of its autonomous driving technology. Despite these challenges, Tesla continues to innovate, focusing on software updates to enhance vehicle capabilities and user experience. Yet, as Tesla pushes the boundaries of autonomous driving, it also faces the task of ensuring robust cybersecurity measures and addressing quality control issues, pivotal for gaining public trust and widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles.
Future of Tesla Steering Wheel
Tesla's vision for the future of steering and overall driving experience is heavily anchored in its pursuit of autonomous driving technology. Central to this vision is the development of features like Autopilot and Full Self-Driving (FSD) capabilities. The company's relentless investment in both hardware, exemplified by Hardware 3.0, and software, notably the FSD computer, demonstrates its commitment to pioneering fully autonomous vehicles. These advancements aim not only to redefine the concept of driving but also to ensure that Tesla vehicles maintain high safety standards. Autopilot and Enhanced Summon are examples of features that enhance safety and convenience, marking steps towards Tesla's ultimate goal of complete driving automation.
Complementing its focus on autonomous driving, Tesla's strategic roadmap includes significant innovations in battery technology, expansion of the Supercharger network, and continuous software evolution through over-the-air updates. The company is revolutionizing battery performance, emphasizing increased energy density and cost efficiency, thereby extending EV range and making electric vehicles more accessible. Tesla's Supercharger network, crucial for long-distance EV travel, is expanding globally, featuring high-speed charging and increasingly targeting urban areas. This expansion is pivotal in alleviating range anxiety among EV users. Furthermore, Tesla's unique approach to software, where vehicles receive regular updates wirelessly, ensures continual enhancement of features, safety, and driving performance. These strategic initiatives not only underscore Tesla's role as a leader in the automotive and energy sectors but also reflect its commitment to sustainable mobility and environmental responsibility.
The comparison between Tesla Yoke and Regular Tesla Steering Wheel
| Feature | Tesla Yoke | Regular Tesla Steering Wheel |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Rectangular with rounded corners, resembles aviation yoke | Traditional circular shape, familiar design |
| Learning Curve | Challenging for many drivers, particularly in basic maneuvers like sharp turns | Generally no learning curve, familiar to most drivers |
| Safety | Concerns over using palm to spin the wheel; safety questioned | Physical stocks and buttons provide tactile feedback and ease of use |
| Visibility | Improved visibility of dashboard and touchscreen | Can partially obstruct view of the vehicle’s dashboard and touchscreen |
| Physical Connection | Physically connected to front wheels, requires more than two full rotations for complete steering | Allows for easy hand-over-hand movement, full range of motion |
| Comfort | Discomfort reported in tight turns and low-speed maneuvers | Universally comfortable for drivers, regardless of previous experience |
| Ergonomics | Initial concerns addressed with updates; ongoing improvements | Traditional design, no major ergonomic issues |
| User Feedback | Mixed reactions; some adapt and appreciate the design, others find it impractical | Widely accepted and preferred for its familiarity and ease of use |
| Future Developments | Potential redesign or alternative options; steer-by-wire system being considered | No significant future developments reported |
FAQs about Tesla Yoke
The Tesla Model S is equipped with a unique stalkless driving feature. This design means that all necessary driving controls are conveniently integrated into the steering yoke (or steering wheel), ensuring easy access and a streamlined driving experience.
Tesla has introduced the option of a conventional, round steering wheel for the Model S and Model X in their online configurator. This change is a response to a series of complaints, some of which are detailed on the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration's (NHTSA) website, particularly on the 2021 Model S information page.
A significant source of discontentment with Tesla's yoke steering setup arises from the fact that it's essentially an unconventional interface attached to a standard electric power steering rack. While its fixed steering ratio is well-suited for highway and performance driving, it proves to be too sluggish in situations requiring precise maneuvering, such as navigating city streets or parking.
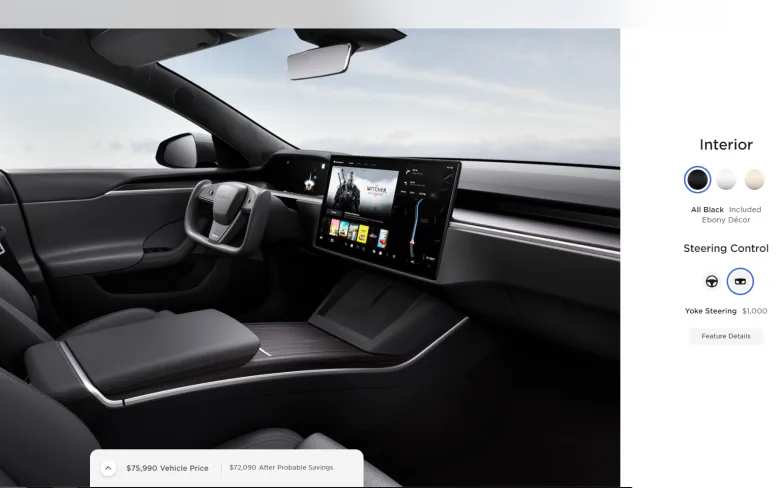
Tesla has raised the price of its yoke steering wheel to $1,000, marking a significant departure from the time when this feature was included as a standard offering not too long ago.
For a deeper dive into the world of electric vehicles, take a look at the article of the Tesla Free Supercharging which offers a detailed look at EVs. Additionally, we made the article about the How Long Does it Take to Charge a Tesla.

















