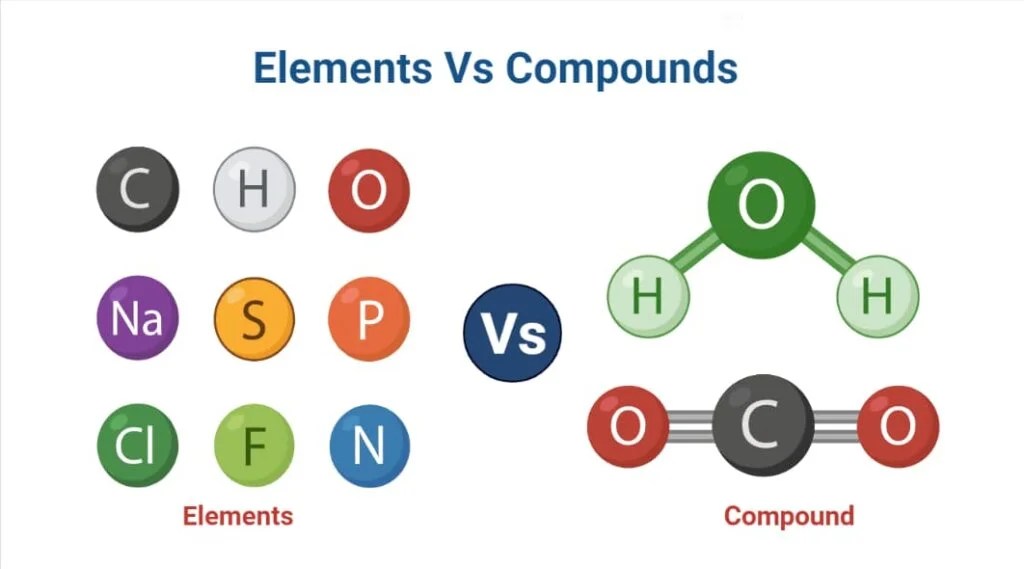
In the world of chemistry, the terms compounds and elements are fundamental concepts that help us understand the composition of matter. Both play crucial roles in the study of substances, their interactions, and their properties. However, many individuals may not fully grasp the differences between these two essential categories of matter. This article will delve into the distinctions between compounds and elements, providing clear definitions, examples, and their significance in various fields.
The first step in understanding the differences between compounds and elements is to define each term accurately. An element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. It consists of only one type of atom, characterized by its atomic number, which determines its unique properties. On the other hand, a compound is a substance formed when two or more elements chemically combine in fixed proportions. Compounds can be broken down into their constituent elements through chemical reactions.
As we explore these concepts further, we will examine the characteristics of elements and compounds, their classifications, and their roles in everyday life. By the end of this article, readers will have a comprehensive understanding of the differences between compounds and elements, enhancing their knowledge of chemistry.
Table of Contents
- Definition of Elements and Compounds
- Characteristics of Elements
- Characteristics of Compounds
- Classification of Elements
- Classification of Compounds
- Examples of Elements and Compounds
- Importance of Understanding Elements and Compounds
- Conclusion
Definition of Elements and Compounds
To fully grasp the differences between compounds and elements, it's essential to understand their definitions. An element is a fundamental substance that cannot be simplified further. Each element is represented by a unique symbol on the periodic table, such as H for hydrogen, O for oxygen, and Fe for iron.
In contrast, a compound is a substance formed when two or more elements chemically bond together. The process of forming compounds involves a chemical reaction that changes the properties of the original elements. For example, when hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) combine, they form water (H2O), a compound with distinct properties different from its constituent elements.
Characteristics of Elements
Elements possess unique characteristics that differentiate them from compounds. Some key characteristics include:
- Homogeneity: Elements are homogenous in nature, consisting of only one type of atom.
- Fixed Properties: Each element has distinct physical and chemical properties, such as boiling and melting points, density, and reactivity.
- Atomic Structure: Elements are made up of atoms, which are the smallest units that retain the properties of the element.
- Cannot be Broken Down: Elements cannot be decomposed into simpler substances using chemical methods.
Characteristics of Compounds
Compounds also exhibit specific characteristics that set them apart from elements:
- Composition: Compounds consist of two or more different elements chemically bonded together.
- Variable Properties: The properties of a compound can differ significantly from those of the individual elements that compose it.
- Chemical Bonds: Compounds are held together by chemical bonds, which can be ionic or covalent in nature.
- Can be Decomposed: Compounds can be broken down into their constituent elements through chemical reactions.
Classification of Elements
Elements can be classified into several categories, including:
- Metals: Generally shiny, malleable, ductile, and good conductors of heat and electricity.
- Nonmetals: Usually dull, brittle, and poor conductors of heat and electricity.
- Metalloids: Elements that exhibit properties of both metals and nonmetals.
Classification of Compounds
Compounds can also be classified based on their composition and structure:
- Inorganic Compounds: Compounds that do not contain carbon-hydrogen bonds, such as salts and minerals.
- Organic Compounds: Compounds that primarily contain carbon and hydrogen, such as hydrocarbons and carbohydrates.
- Ionic Compounds: Compounds formed by the transfer of electrons from one atom to another.
- Covalent Compounds: Compounds formed by the sharing of electrons between atoms.
Examples of Elements and Compounds
Understanding real-world examples can further clarify the differences between elements and compounds:
Examples of Elements
- Hydrogen (H)
- Oxygen (O)
- Carbon (C)
- Gold (Au)
Examples of Compounds
- Water (H2O)
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
- Sodium Chloride (NaCl)
- Glucose (C6H12O6)
Importance of Understanding Elements and Compounds
Grasping the differences between elements and compounds is vital in various fields:
- Chemistry: Fundamental to understanding chemical reactions and processes.
- Biology: Essential for comprehending biological molecules and their functions.
- Environmental Science: Helps in analyzing pollutants and their impacts on ecosystems.
- Medicine: Crucial for drug development and understanding biochemical pathways.
Conclusion
In summary, compounds and elements are two distinct categories of matter that play crucial roles in chemistry and our understanding of the natural world. Elements are pure substances that cannot be broken down, while compounds consist of two or more elements chemically combined. Understanding these differences is essential for various scientific disciplines and everyday applications. We encourage readers to explore further, engage with the material, and apply their knowledge in practical scenarios. Feel free to leave a comment, share this article, or check out other related content on our site!
Thank you for reading! We hope to see you again soon for more insightful articles.
- Kristy Mcnichol
- 1470855 Zack Lugos Biography Age Height Net Worth Girlfriend Brother
- Oleksandr Zinchenko
- 1230857 Tyler Perry Net Worth Age Height House Wife Son
- La Freeway Protest
- Josh Allen Old Tweets
- Thay Ksada
- 1534693 Piece Female Characters Deserve Attention
- Tiffany Link Earrings