When it comes to the world of chemistry, the term "g/mol" is frequently encountered, and understanding its significance is crucial for students and professionals alike. This unit, which stands for grams per mole, plays a vital role in various chemical calculations, including stoichiometry, molecular weight determinations, and more. In this article, we will delve into the detailed aspects of g/mol, its applications, and why it is essential in the field of science.
We will explore the concept of molar mass, how to calculate it, and its importance in both educational and practical contexts. Additionally, we will provide insights into the relationship between g/mol and other related concepts in chemistry. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of g/mol and its relevance in chemical sciences.
Whether you are a student preparing for exams, a teacher looking for resources, or simply someone interested in learning more about chemistry, this article is tailored to provide you with valuable information. Let’s embark on this enlightening journey into the world of g/mol!
Table of Contents
- What is g/mol?
- Importance of g/mol in Chemistry
- Calculating Molar Mass
- Examples of g/mol in Real-life Applications
- g/mol vs. Other Units of Measurement
- Common Mistakes in Using g/mol
- Resources for Learning More About g/mol
- Conclusion
What is g/mol?
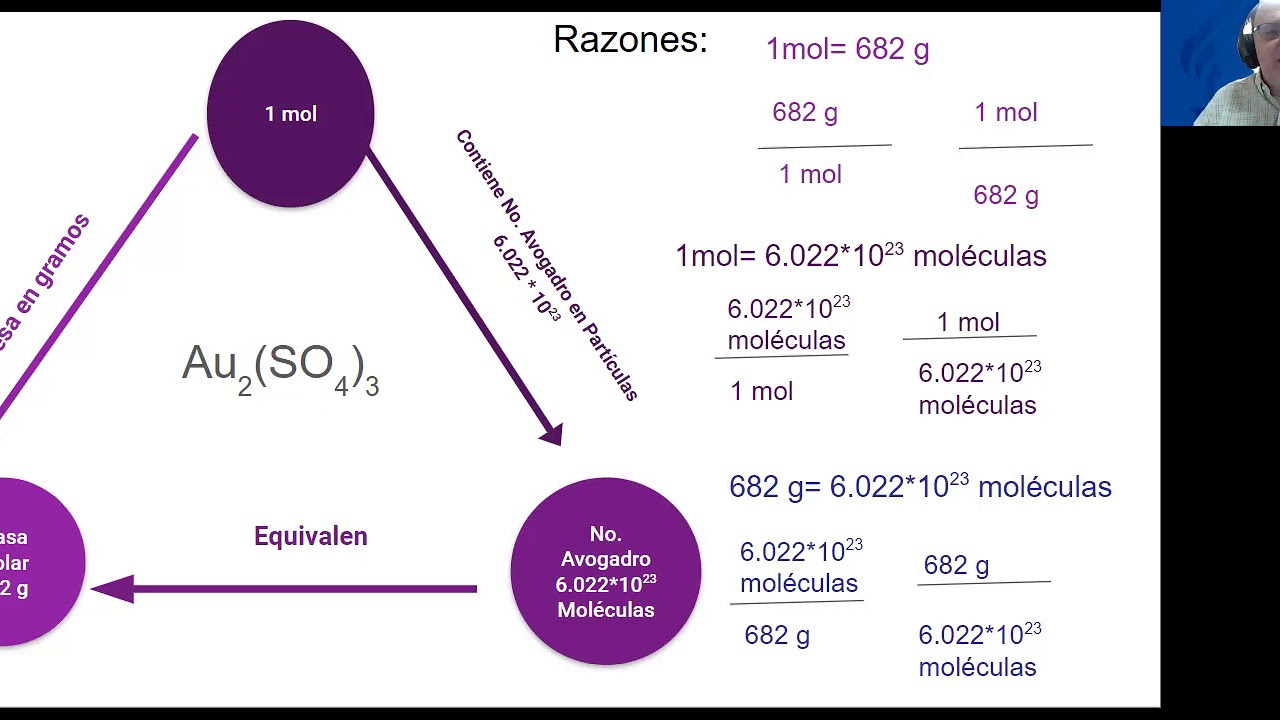
The unit g/mol, or grams per mole, is a measure used to express the mass of a substance in grams relative to the amount of substance in moles. It provides a way to convert between the mass of a substance and the number of particles (atoms, molecules, or ions) contained within that substance.
One mole of any substance contains approximately 6.022 x 1023 entities (Avogadro's Number). Therefore, the molar mass of a substance tells you how many grams one mole of that substance weighs. For example, the molar mass of water (H2O) is about 18.02 g/mol, meaning one mole of water weighs 18.02 grams.
Definition and Calculation of Molar Mass
Molar mass is calculated by summing the atomic masses of all the atoms in a molecule. The atomic mass can be found on the periodic table of elements, usually expressed in atomic mass units (amu). To convert this to g/mol, you simply use the same numerical value, as 1 amu is equivalent to 1 g/mol.
Importance of g/mol in Chemistry
Understanding g/mol is fundamental for anyone studying chemistry. Here are a few reasons why this unit is critically important:
- Stoichiometry: g/mol is essential for balancing chemical equations and determining the quantities of reactants and products involved in chemical reactions.
- Solution Concentrations: Molar mass is crucial in calculating the concentrations of solutions, allowing chemists to prepare solutions of desired molarity.
- Gas Laws: In gas calculations, molar mass is used to relate the mass of a gas to its volume and pressure, aiding in the understanding of gas behaviors.
Calculating Molar Mass
To calculate the molar mass of a compound, follow these steps:
- Identify the chemical formula of the compound.
- Use the periodic table to find the atomic mass of each element in the compound.
- Multiply the atomic mass of each element by the number of times that element appears in the chemical formula.
- Add all of these values together to obtain the total molar mass of the compound.
Example Calculation
For example, to calculate the molar mass of carbon dioxide (CO2), you would do the following:
- Carbon (C): 1 x 12.01 g/mol = 12.01 g/mol
- Oxygen (O): 2 x 16.00 g/mol = 32.00 g/mol
- Total: 12.01 g/mol + 32.00 g/mol = 44.01 g/mol
Examples of g/mol in Real-life Applications
g/mol has numerous applications in both laboratory and real-world settings:
- Pharmaceuticals: The development of medications requires precise calculations of molar mass to ensure the correct dosage and efficacy.
- Environmental Science: Understanding the molar mass of pollutants helps in assessing their impact on the environment and human health.
- Food Chemistry: Accurate molar mass calculations are essential in food production and safety assessments.
g/mol vs. Other Units of Measurement
While g/mol is widely used, there are other units that may be encountered in various scientific contexts:
- kg/mol: Often used in larger-scale chemical processes, especially in industrial applications.
- mol/L: Used to express concentration, indicating moles of solute per liter of solution.
Common Mistakes in Using g/mol
Here are some common pitfalls to avoid when working with g/mol:
- Confusing g/mol with molarity (mol/L).
- Forgetting to sum the total atomic masses correctly when calculating molar mass.
- Assuming that all compounds have the same molar mass based on their chemical formula without considering their molecular complexity.
Resources for Learning More About g/mol
To deepen your understanding of g/mol and related concepts, consider the following resources:
- ChemSpider - A free chemical structure database.
- PubChem - A comprehensive resource for chemical information.
- Khan Academy - Offers free courses on chemistry topics, including stoichiometry.
Conclusion
In conclusion, g/mol is a crucial unit in chemistry that aids in understanding the relationship between mass and the number of particles in a substance. Recognizing its importance in various applications, from stoichiometry to pharmaceuticals, is essential for anyone engaged in the field of chemistry.
If you found this article helpful, we invite you to leave a comment, share it with others, or explore more articles on our site for further learning. Your feedback is invaluable, and we look forward to bringing you more insightful content!
Thank you for taking the time to read our comprehensive guide on g/mol. We hope to see you back on our site for more educational resources!
- Josh Allen Old Tweets
- Kristy Mcnichol
- Oleksandr Zinchenko
- 1470855 Zack Lugos Biography Age Height Net Worth Girlfriend Brother
- Thay Ksada
- 1534693 Piece Female Characters Deserve Attention
- Tiffany Link Earrings
- La Freeway Protest
- 1230857 Tyler Perry Net Worth Age Height House Wife Son