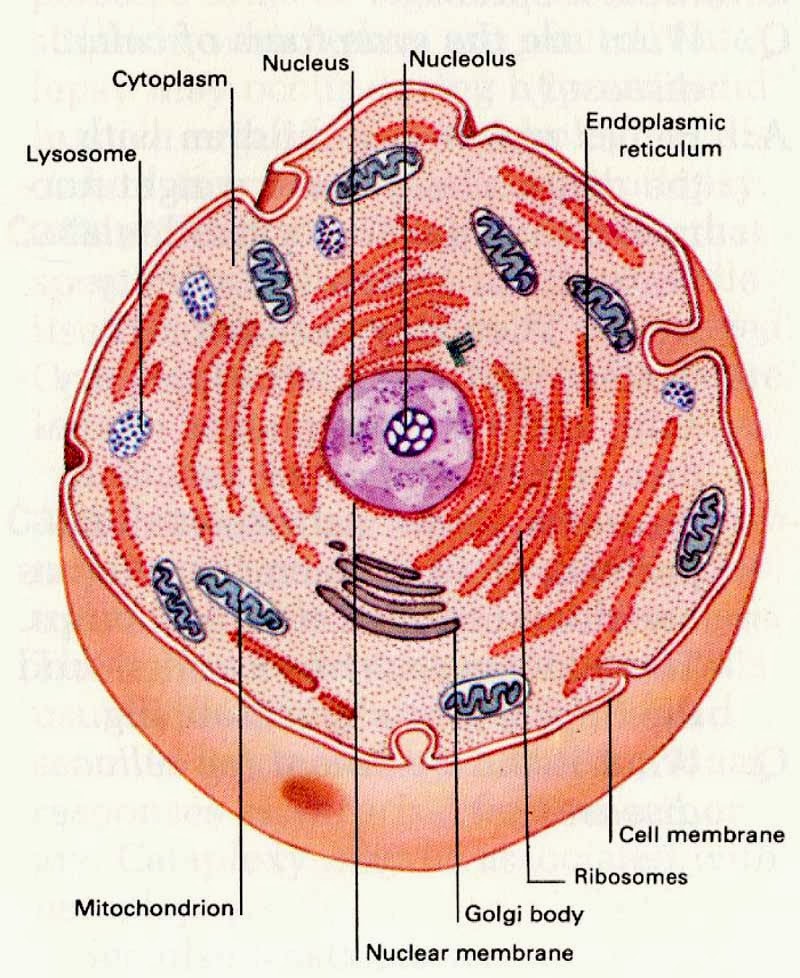
Understanding the appearance and characteristics of granular cytoplasm is crucial for anyone studying cell biology, histology, or related fields. Granular cytoplasm is an essential component of cells, influencing various cellular functions and processes. In this article, we will explore what granular cytoplasm is, its features, and its significance in cellular activities. By the end, you will have a comprehensive understanding of this important aspect of cell structure.
Granular cytoplasm refers to the portion of cytoplasm that contains various granules and organelles, contributing to the cell's overall function and metabolic processes. Its appearance can vary significantly depending on the cell type, the presence of specific granules, and the physiological state of the cell. This article aims to provide a thorough overview of granular cytoplasm, examining its characteristics, functions, and implications in health and disease.
Whether you are a student, a researcher, or simply someone with a keen interest in biology, this article will serve as a valuable resource. We will break down the topic into manageable sections, ensuring clarity and depth while maintaining an engaging narrative. So, let’s dive into the fascinating world of granular cytoplasm!
Table of Contents
- Definition of Granular Cytoplasm
- Characteristics of Granular Cytoplasm
- Types of Granular Cytoplasm
- Functions of Granular Cytoplasm
- Visualization Techniques
- Importance in Health and Disease
- Current Research on Granular Cytoplasm
- Conclusion
Definition of Granular Cytoplasm
Granular cytoplasm is defined as the cytoplasmic region in a cell that contains numerous small particles or granules. These granules may include ribosomes, organelles, or storage materials like glycogen. The presence of these structures gives the cytoplasm a 'granular' appearance under the microscope, distinguishing it from other types of cytoplasmic regions.
Characteristics of Granular Cytoplasm
The granular cytoplasm has several key characteristics that set it apart from other cytoplasmic regions:
- Granularity: The most defining feature is the presence of granules that can vary in size and density.
- Composition: It is rich in ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, and other organelles that play vital roles in protein synthesis and metabolism.
- Variability: The composition and appearance of granular cytoplasm can change based on the cell type and its functional state.
Types of Granular Cytoplasm
Granular cytoplasm can be categorized based on the types of granules present within it. Two significant types include:
Ribosomes in Granular Cytoplasm
Ribosomes are the primary granules found in granular cytoplasm. They are essential for protein synthesis, translating mRNA into polypeptide chains. Ribosomes can be free-floating in the cytoplasm or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum, forming rough ER.
Glycogen Granules
Glycogen granules serve as energy storage in cells, particularly in liver and muscle cells. These granules can be visualized with specific staining techniques, making them a vital aspect of studying cellular metabolism.
Functions of Granular Cytoplasm
The granular cytoplasm plays several critical roles in cellular function:
- Protein Synthesis: Granular cytoplasm is the site where proteins are synthesized, thanks to the presence of ribosomes.
- Metabolism: The granules contribute to various metabolic pathways, including energy production and storage.
- Cellular Signaling: Granules can also play a role in intracellular signaling processes, affecting how cells respond to external stimuli.
Visualization Techniques
To observe granular cytoplasm and its components, several visualization techniques are employed:
- Light Microscopy: Basic staining methods can highlight the granularity of cytoplasm.
- Electron Microscopy: Provides a high-resolution view of granules and organelles, allowing for detailed structural analysis.
- Fluorescence Microscopy: Specific dyes can be used to target granules, providing insights into their function and distribution.
Importance in Health and Disease
The study of granular cytoplasm is vital for understanding various health conditions:
- Cellular Dysfunction: Abnormalities in granular cytoplasm can indicate cellular dysfunction and diseases.
- Diagnosis: Examining granular cytoplasm can aid in diagnosing conditions such as cancer and metabolic disorders.
- Therapeutic Targets: Understanding the role of granules may lead to new therapeutic strategies in treating diseases.
Current Research on Granular Cytoplasm
Ongoing research continues to uncover the complexities of granular cytoplasm:
- Granule Dynamics: Studies focus on how granules are formed, maintained, and degraded within cells.
- Role in Diseases: Research explores the link between granular cytoplasm and various diseases, including neurodegenerative disorders.
- Technological Advances: New imaging technologies enhance our understanding of cellular structures and functions.
Conclusion
In summary, granular cytoplasm is a critical component of cellular structure, playing essential roles in protein synthesis, metabolism, and cellular signaling. Understanding its characteristics and functions is vital for advancing our knowledge of cell biology and its implications in health and disease. We encourage you to engage with this topic further by leaving comments, sharing this article, or exploring related articles on our site.
Thank you for reading! We hope you found this article informative and valuable. Don’t hesitate to return for more insights into the fascinating world of biology.
- Kristy Mcnichol
- Oleksandr Zinchenko
- 1534693 Piece Female Characters Deserve Attention
- Tiffany Link Earrings
- Josh Allen Old Tweets
- Thay Ksada
- 1230857 Tyler Perry Net Worth Age Height House Wife Son
- 1470855 Zack Lugos Biography Age Height Net Worth Girlfriend Brother
- La Freeway Protest