Prejudice and racism are two terms often used interchangeably, but they represent different concepts that have significant implications for individuals and society. Understanding the differences between these two terms is crucial for fostering a more inclusive and equitable society. In this article, we will delve into the definitions, manifestations, and impacts of prejudice and racism, as well as explore ways to combat these harmful attitudes.
Throughout history, prejudice and racism have been at the forefront of societal issues, leading to discrimination and inequality. This article will provide a comprehensive analysis of these concepts, highlighting their unique characteristics and the ways they intersect. By examining these issues in depth, we aim to raise awareness and promote understanding, ultimately contributing to a more just society.
Join us as we navigate the complex landscape of prejudice versus racism, equipping ourselves with the knowledge necessary to challenge these negative attitudes and work towards a more inclusive future.
Table of Contents
- 1. Definition of Prejudice
- 2. Definition of Racism
- 3. Manifestations of Prejudice and Racism
- 4. Causes of Prejudice and Racism
- 5. Impacts of Prejudice and Racism
- 6. Combating Prejudice and Racism
- 7. The Role of Education in Addressing Prejudice and Racism
- 8. Conclusion
1. Definition of Prejudice
Prejudice refers to preconceived opinions or judgments about individuals or groups based on characteristics such as race, ethnicity, gender, religion, or sexual orientation. These judgments are often formed without sufficient knowledge, understanding, or experience. Prejudice can manifest as negative attitudes, beliefs, or feelings towards others and can be both conscious and unconscious.
Prejudice can be categorized into several types:
- Racial Prejudice: Negative beliefs or attitudes towards individuals based on their race.
- Gender Prejudice: Discrimination based on gender, typically against women.
- Religious Prejudice: Negative attitudes towards individuals based on their religious beliefs.
- Homophobia: Prejudice against individuals based on their sexual orientation.
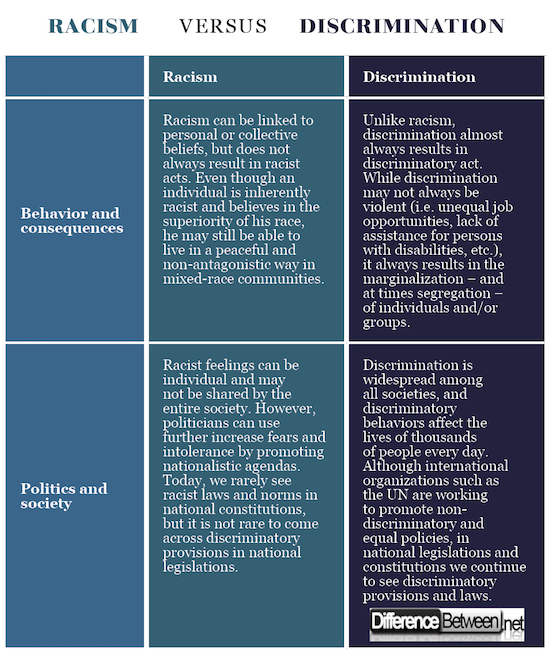
2. Definition of Racism
Racism, on the other hand, is a systemic belief that one race is inherently superior or inferior to others. This belief can manifest in various forms, including individual racism (personal beliefs and actions) and institutional racism (policies and practices that perpetuate racial inequality). Racism is often embedded in societal structures and institutions, leading to discrimination and disadvantage for marginalized racial groups.
Racism can be expressed in different ways:
- Individual Racism: Personal prejudices or discriminatory behaviors towards individuals based on their race.
- Institutional Racism: Systems and policies that maintain racial inequality within institutions such as education, healthcare, and law enforcement.
- Cultural Racism: The belief that one culture is superior to others, leading to the marginalization of different cultural practices.
3. Manifestations of Prejudice and Racism
Both prejudice and racism can manifest in various ways, impacting individuals and communities. Understanding these manifestations is essential for addressing and combating them effectively.
3.1. Manifestations of Prejudice
Prejudice can manifest in several forms, including:
- Stereotyping: Making generalized assumptions about individuals based on their group membership.
- Discrimination: Treating individuals unfairly based on their characteristics.
- Microaggressions: Subtle, often unintentional, comments or actions that convey derogatory messages.
3.2. Manifestations of Racism
Racism can be more overt or institutionalized, including:
- Hate Crimes: Violent acts directed towards individuals based on their race.
- Racial Profiling: Law enforcement practices that target individuals based on their race.
- Systemic Inequalities: Disparities in wealth, education, and healthcare based on race.
4. Causes of Prejudice and Racism
Understanding the root causes of prejudice and racism is vital in addressing these issues. Several factors contribute to the formation of prejudiced attitudes and racist beliefs:
- Socialization: Individuals often learn prejudiced beliefs from family, peers, and media.
- Ignorance: Lack of knowledge or exposure to diverse groups can breed prejudice.
- Fear: Fear of the unknown or unfamiliar can lead to negative attitudes towards others.
- Scapegoating: Blaming a specific group for societal problems or personal frustrations can fuel racism.
5. Impacts of Prejudice and Racism
The impacts of prejudice and racism are profound, affecting individuals, communities, and society as a whole. Some of the significant consequences include:
- Mental Health Issues: Individuals who experience prejudice and racism may suffer from anxiety, depression, and other mental health challenges.
- Social Division: Prejudice and racism can create divisions within society, leading to conflict and tension.
- Economic Disparities: Systemic racism contributes to economic inequalities, limiting opportunities for marginalized groups.
- Educational Barriers: Prejudice can affect educational access and quality for marginalized students.
6. Combating Prejudice and Racism
Addressing prejudice and racism requires collective effort and commitment from individuals and society. Here are some strategies to combat these harmful attitudes:
- Education and Awareness: Promoting education about diversity and inclusion can help challenge prejudiced beliefs.
- Open Dialogue: Encouraging conversations about race and prejudice can foster understanding and empathy.
- Policy Change: Advocating for policies that promote equality and address systemic racism is essential.
- Support for Marginalized Groups: Providing resources and support for marginalized communities can help combat the effects of prejudice and racism.
7. The Role of Education in Addressing Prejudice and Racism
Education plays a crucial role in addressing and combating prejudice and racism. By promoting awareness and understanding of these issues, educational institutions can contribute to building a more inclusive society.
Some ways education can help include:
- Curriculum Development: Incorporating diverse perspectives and histories can challenge stereotypes and promote understanding.
- Training Programs: Providing anti-bias training for educators can help create a more inclusive learning environment.
- Community Engagement: Encouraging partnerships between schools and communities can foster collaboration and understanding.
8. Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the differences between prejudice and racism is essential for fostering a more equitable and inclusive society. While prejudice involves preconceived judgments based on characteristics, racism encompasses systemic beliefs and practices that perpetuate inequality. By raising awareness and promoting education, we can work collectively to combat these harmful attitudes and create a more just world.
We encourage you to share your thoughts in the comments section, engage in conversations about these important issues, and explore additional resources to further your understanding.
Thank you for taking the time to read this article! We hope to see you back here for more insightful discussions and information.
- La Freeway Protest
- 1470855 Zack Lugos Biography Age Height Net Worth Girlfriend Brother
- 1534693 Piece Female Characters Deserve Attention
- Oleksandr Zinchenko
- 1230857 Tyler Perry Net Worth Age Height House Wife Son
- Kristy Mcnichol
- Tiffany Link Earrings
- Josh Allen Old Tweets
- Thay Ksada
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/racism-vs-prejudice-3026086-v3-5b562afa46e0fb005b3ca05e.png)
