Understanding the properties of liquids is essential in various fields including science, engineering, and even daily life. When we talk about liquids, two important characteristics come into play: volume and density. These properties not only define how we interact with liquids but also impact their applications in different scenarios. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of liquids, exploring whether they possess high or low volume and density, and the implications of these properties in real-world contexts.
To begin, it’s crucial to understand what volume and density mean in the context of liquids. Volume refers to the amount of space a liquid occupies, while density is the mass of the liquid per unit volume. These two characteristics are interrelated and can vary significantly among different types of liquids. Throughout this article, we will discuss how various factors influence the volume and density of liquids and why these properties are crucial for both scientific and practical applications.
As we proceed, we will provide detailed insights into the measurements, comparisons, and real-world implications of liquid volume and density, making it easier for readers to grasp these concepts. Whether you are a student, a professional, or simply someone curious about the nature of liquids, this comprehensive guide is designed to enhance your understanding of these essential properties.
Table of Contents
- 1. Understanding Liquid Properties
- 2. Definition of Volume in Liquids
- 3. Definition of Density in Liquids
- 4. Factors Affecting Density of Liquids
- 5. Volume vs. Density: Key Differences
- 6. Applications of Liquid Volume and Density
- 7. Common Liquids and Their Properties
- 8. Conclusion
1. Understanding Liquid Properties
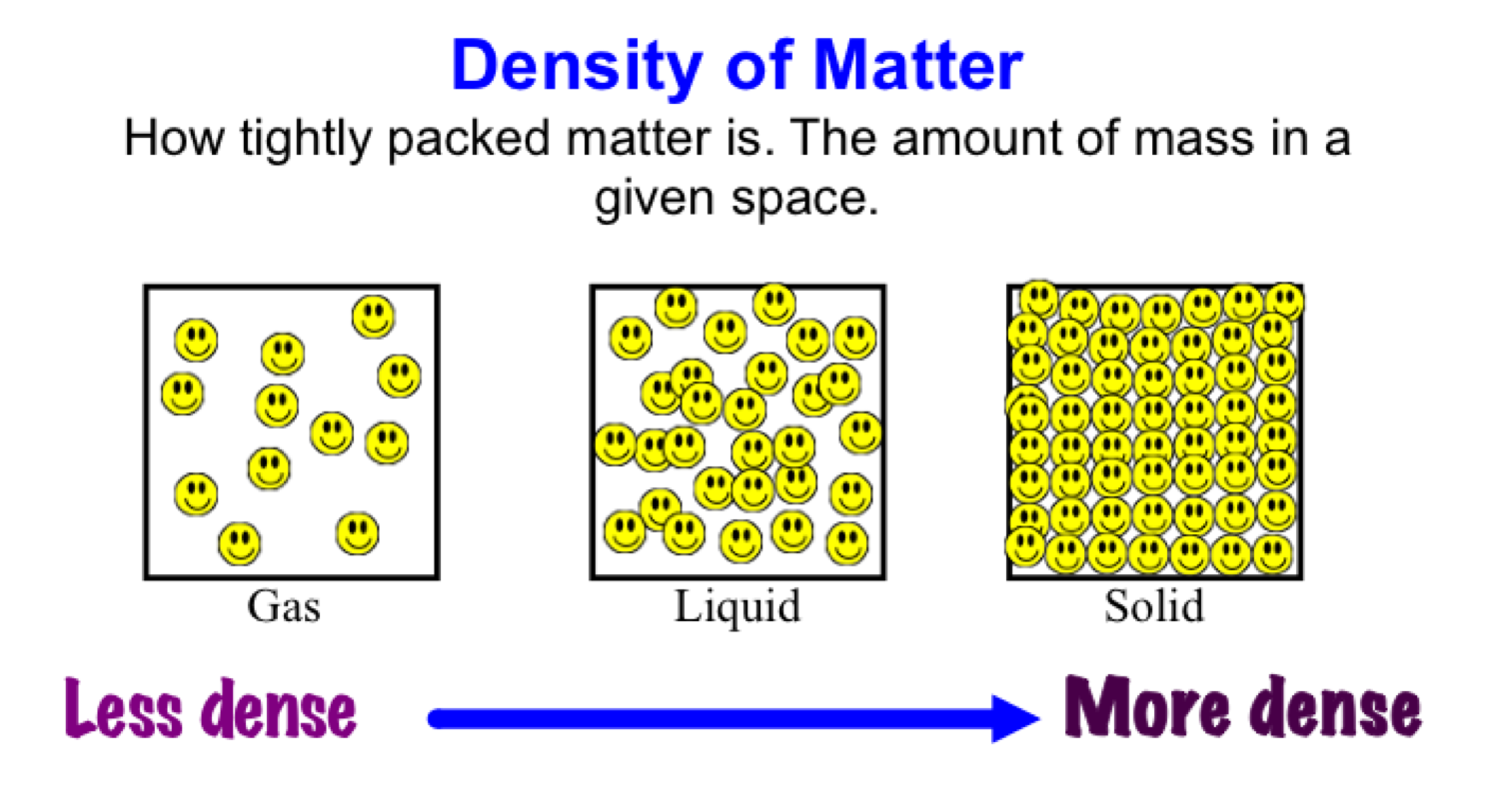
Liquids have unique properties that distinguish them from solids and gases. Understanding these properties is essential, especially in scientific and industrial applications. The primary properties of liquids include fluidity, incompressibility, and the ability to take the shape of their container. Among these, volume and density are critical characteristics that dictate how liquids behave in different environments.
2. Definition of Volume in Liquids
Volume is a measure of the space occupied by a liquid. It is typically expressed in liters (L), milliliters (mL), or cubic centimeters (cm³). The volume of a liquid can be easily measured using various tools such as graduated cylinders, pipettes, and volumetric flasks. The volume of a liquid can change based on temperature and pressure, which can lead to expansion or contraction.
Measuring Liquid Volume
- Graduated Cylinders: Commonly used for precise measurements.
- Pipettes: Useful for transferring small volumes of liquid.
- Volumetric Flasks: Ideal for preparing solutions with specific concentrations.
3. Definition of Density in Liquids
Density is defined as the mass of a substance per unit volume, usually expressed in grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³) or kilograms per liter (kg/L). The formula to calculate density is:
Density (ρ) = Mass (m) / Volume (V)
For liquids, density can be influenced by temperature, pressure, and the composition of the liquid itself. For instance, when heating a liquid, its density may decrease as the molecules move farther apart.
Calculating Density
To calculate the density of a liquid, follow these simple steps:
- Weigh the liquid using a balance to determine its mass.
- Measure the volume of the liquid using appropriate measuring tools.
- Apply the density formula to find the density.
4. Factors Affecting Density of Liquids
The density of a liquid can be affected by various factors, including:
- Temperature: As temperature increases, most liquids expand, which can reduce density.
- Pressure: Increased pressure can compress a liquid, potentially increasing its density.
- Composition: The molecular composition of a liquid plays a significant role in determining its density. For example, saltwater is denser than freshwater due to the dissolved salts.
5. Volume vs. Density: Key Differences
While both volume and density are essential properties of liquids, they represent different concepts. Volume is about how much space a liquid occupies, while density is about how much mass is contained within that volume. For instance, a large volume of a liquid does not necessarily indicate high density. Understanding the differences between these two properties is crucial for various applications, including engineering and environmental science.
6. Applications of Liquid Volume and Density
Liquid volume and density have numerous applications across various fields:
- Chemical Engineering: Understanding the density of substances is vital for designing chemical processes.
- Environmental Science: Density measurements help assess pollution levels in water bodies.
- Food Industry: Volume and density are important in food processing and packaging.
7. Common Liquids and Their Properties
Here are some common liquids and their typical densities:
| Liquid | Density (g/cm³) |
|---|---|
| Water | 1.00 |
| Olive Oil | 0.91 |
| Alcohol (Ethanol) | 0.789 |
| Syrup | 1.3 |
8. Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding whether liquids have high or low volume and density is essential for various scientific and practical applications. By grasping the definitions, factors influencing these properties, and their differences, readers can better appreciate the role of liquids in our daily lives and industries. We encourage you to explore further and engage with this fascinating topic by sharing your thoughts or experiences in the comments below!
Thank you for reading! We hope you found this article informative and engaging. Be sure to check out our other articles for more insights into the world of science and liquids!
- 1534693 Piece Female Characters Deserve Attention
- 1230857 Tyler Perry Net Worth Age Height House Wife Son
- La Freeway Protest
- Thay Ksada
- Josh Allen Old Tweets
- 1470855 Zack Lugos Biography Age Height Net Worth Girlfriend Brother
- Tiffany Link Earrings
- Oleksandr Zinchenko
- Kristy Mcnichol